Basics of Mobile Repairing
Here we will take you through the Basic to Advanced Level Mobile Repairing Course.
One can become an entrepreneur & open a mobile service centre after completing this course. Let us start the chapter with the Fundamentals of Electronics & the Basics of Mobile Repairing.



What is Electronics? How it has impacted today’s technology?
Electronics is the science which deals with the study of the flow of electrons in the circuit. Nowadays all the electronics devices are made from Semiconductor material which is manufactured using silicon after a series of processes.
To the surprise, silicon material is the second most available resource in the world.
All components in the Mobile PCB board are made from Semiconductor devices which are designed in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) & the components designed described as SMD which is Surface Mount Device.
Let us now see different types of components made from semiconductor material. This falls under the category Active Elements & Passive Elements.
Active Elements:
Diode, Transistor & IC (Integrated Circuit) are Active elements that would operate on power. The main function of these elements amplifies the given supply/signal & also restricts the voltage that passes in the reverse direction.
Diode:
- Conversion of AC to DC
- Rectification / Switching
- Pass Voltage in Forward bias
- Restrict Voltage in Reverse bias
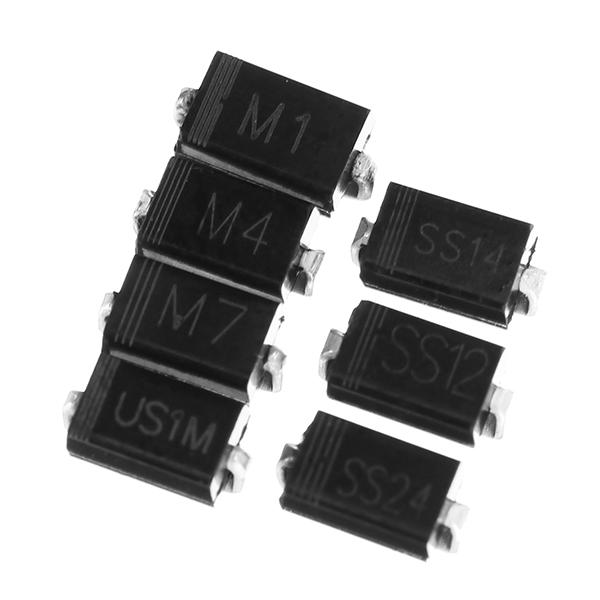


Transistor
There are two types of transistors namely Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) & Field Effect Transistor (FET). These Transistors are further classified into two types.
Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT):
- PNP
- NPN
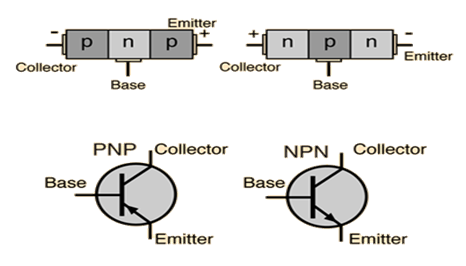


Field Effect Transistor (FET):
- MOSFET
- JFET
MOSFET transistors are widely used in mobiles & also thousands of transistors are incorporated in IC’s for various functions.



Integrated Circuit
IC’s are made from semiconductor wafer on which thousands or millions of tiny resistors, capacitors, and transistors are fabricated.
An IC can function as an amplifier, oscillator, timer, counter, CPU / Memory.
IC’s are classified into three types:
- Dual Inline Package (DIP) IC
- Quad inline Package (QIP) IC
- Ball Grid Array IC
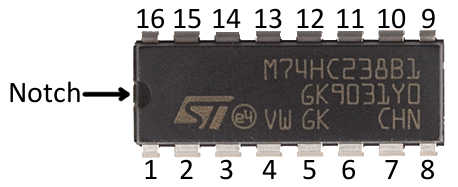
Dual Inline Package IC
Integrated Circuit or CHIP that contains a Large circuit compressed in a single millimeter-sized substrate. Dual Inline Package (DIP) ICs.


QIP Package IC
Integrated Circuit or CHIP that contains Large circuit compressed in a single millimeter-sized substrate. Quad Inline package (QIP) ICs.
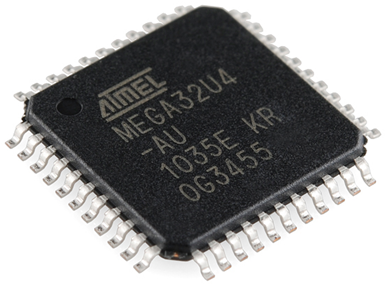


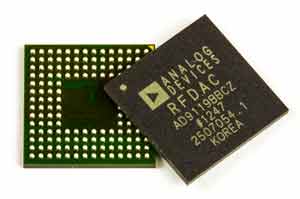
Ball Grid Array (BGA) IC
Integrated Circuits are comes in different size and different package, it fully depends on application of that particular IC.
As day by day new technology getting evolved, BGA ICs plays a major role wherein most of the section like Power management Section, Network Section & Memory / Storage sections are incorporated in BGA IC’s


Passive Elements:
Resistor, Capacitor, Inductors are Passive Elements that does not need any power to operate but when we apply power(alternating supply or direct current supply) it reduce the amplitude or reacts like a barrier to the voltage and current, some time passive components stores electrical energy as a magnetic or field charge and discharges. It consumes power but does not increase power.
Resistor:
Resistor limits or regulates the flow of electrical current in an electronic circuit.



Inductor
- Energy is stored in a magnetic field in the coil as long as current flows. •
- Block AC & Pass DC
- DC – DC Boost Voltage
- Signal Filter (High / Low Frequency)



Capacitor
- Charging / Discharging of Voltage
- Block DC & Pass AC
- Filter AC Voltage
- Balance Voltage (Store DC voltage / Balance Voltage for smooth circuit operation)



We have learned the fundamental of electronics which is important in the Basics of Mobile Repairing . Now we will learn briefly on the functions of these components in the mobile device in the upcoming chapter.

